- Install Android On Mac
- Virtual Android On Mac Free
- Virtual Android On Android
- Virtual Android On Mac Desktop
Jul 26, 2021 Virtualbox happens to be one of the complicated Android software for Mac. Technically it’s not an emulator but helps you create one though. You will require number of other tools like Adroid-x86.org to work along with VirtualBox. It depends on you as how you can use commands after getting those tools. Here are the best virtual machine apps for Mac. VirtualBox is a free and open source virtual machine software from Oracle. It’s designed with developers and IT professionals in mind, so VirtualBox provides you with a great deal of control over your virtual environments. VirtualBox supports a great number of guest operating.
Installing Android on a Mac Installing Virtualbox on the Mac. To start, download Virtualbox for OS X, free of charge, and open the downloaded image. Run the Virtualbox.pkg package and follow the on-screen prompts to install the app on the Mac. Download Android for x86, a modified version of Android that's developed to run on Intel-based computers. The Android Studio setup wizard will start, follow the instructions on the screen. (Or hit “next” until it says “install”.) Tap on “install” when prompted and the Android SDK will start installing on your computer. This may take a few minutes. Click on “finish” and the Android SDK will start. Best Android Emulator for Mac – Ultimate Edition. So, here goes the list of Top Android Emulators Mac. Go through the list mentioned below and find one that suits you the best. Start playing Android Games on Mac or Install Google Play Store and use any android apps on Mac. Bluestacks for Mac.
BrowserCam provides you Android Device Manager for PC (computer) download for free. Google Inc. launched Android Device Manager app for Android OS together with iOS but you might also install Android Device Manager on PC or MAC. You’ll find few essential points listed below that you will have to implement before you begin to download Android Device Manager PC.
Install Android Studio on Mac OS X. The purpose of this section is to guide you to install in your development environment all the dependencies for Android development. The fastest way is to download and install Android Studio. Latest current version for Android Studio is available at.
Out of various paid and free Android emulators available for PC, it’s not a simple step like you imagine to pick the ideal Android emulator that works well with your PC. To assist you we will recommend either Bluestacks or Andy android emulator, each of them are compatible with MAC and windows os. We inform you to initially explore the suggested OS requirements to install the Android emulator on PC then download if only your PC fulfills the recommended Operating system requirements of the emulator. It’s very easy to install the emulator when you’re all set and barely requires few minutes or so. Simply click 'Download Android Device Manager APK' icon to start downloading the apk file on your PC.
How to Download Android Device Manager for PC or MAC:
1. Download BlueStacks for PC considering the download option offered in this particular web site.
2. As soon as the download process is over open up the installer to start out with the install process.
3. Read the initial two steps and click 'Next' to go to the third step of set up.
4. In the very final step select the 'Install' option to get started with the install process and click 'Finish' anytime its finally finished.At the last & final step simply click on 'Install' to begin the final install process and you’ll be able to click on 'Finish' in order to finish the installation.
5. With the windows start menu or alternatively desktop shortcut begin BlueStacks app.
6. Before you install Android Device Manager for pc, you’ll have to connect BlueStacks Android emulator with a Google account.
7. Next, you must be brought to google playstore page which lets you do a search for Android Device Manager app using search bar and install Android Device Manager for PC or Computer.
After you installed the Android emulator, you can also make use of the APK file to be able to install Android Device Manager for PC either by clicking on apk or by opening it via BlueStacks Android emulator due to the fact that a portion of your preferred Android games or apps probably aren’t accessible in google playstore because they do not comply with Developer Policies. You can stick to the above exact same steps even though you want to opt for Andy OS emulator or if you choose to choose free download and install Android Device Manager for MAC.
- Get the Flutter SDK
- iOS setup
- Android setup
System requirements
To install and run Flutter,your development environment must meet these minimum requirements:
- Operating Systems: macOS (64-bit)
- Disk Space: 2.8 GB (does not include disk space for IDE/tools).
- Tools: Flutter depends on these command-line tools being availablein your environment.
bashcurlgit2.xmkdirrmunzipwhich
Get the Flutter SDK
Download the following installation bundle to get the lateststable release of the Flutter SDK:
For other release channels, and older builds,see the SDK releases page.
Extract the file in the desired location, for example:
If you don’t want to install a fixed version of the installation bundle, you can skip steps 1 and 2. Instead, get the source code from the Flutter repoon GitHub with the following command:
You can also change branches or tags as needed.For example, to get just the stable version:
Add the
fluttertool to your path:This command sets your
PATHvariable for thecurrent terminal window only.To permanently add Flutter to your path, seeUpdate your path.Optionally, pre-download development binaries:
Powerful Mac apps that won't break the bank. There’s something of a misconception when it comes. Free applications download for mac.
The
fluttertool downloads platform-specific development binaries asneeded. For scenarios where pre-downloading these artifacts is preferable(for example, in hermetic build environments,or with intermittent network availability), iOSand Android binaries can be downloaded ahead of time by running:For additional download options, see
flutter help precache.
You are now ready to run Flutter commands!
Note: To update an existing version of Flutter, see Upgrading Flutter.
Run flutter doctor
Run the following command to see if there are any dependencies you need toinstall to complete the setup (for verbose output, add the -v flag):
This command checks your environment and displays a report to the terminalwindow. The Dart SDK is bundled with Flutter; it is not necessary to installDart separately. Check the output carefully for other software you mightneed to install or further tasks to perform (shown in bold text).
For example:
The following sections describe how to perform these tasks and finish the setupprocess.
Once you have installed any missing dependencies, run the flutter doctorcommand again to verify that you’ve set everything up correctly.
Warning: The flutter tool uses Google Analytics to anonymously report feature usage statistics and basic crash reports. This data is used to help improve Flutter tools over time.
Flutter tool analytics are not sent on the very first run. To disable reporting, type flutter config --no-analytics. To display the current setting, type flutter config. If you opt out of analytics, an opt-out event is sent, and then no further information is sent by the Flutter tool.
By downloading the Flutter SDK, you agree to the Google Terms of Service. Note: The Google Privacy Policy describes how data is handled in this service.
Moreover, Flutter includes the Dart SDK, which may send usage metrics and crash reports to Google.
Update your path
You can update your PATH variable for the current session atthe command line, as shown in Get the Flutter SDK.You’ll probably want to update this variable permanently,so you can run flutter commands in any terminal session.
The steps for modifying this variable permanently forall terminal sessions are machine-specific.Typically you add a line to a file that is executedwhenever you open a new window. For example:
- Determine the directory where you placed the Flutter SDK.You need this in Step 3.
- Open (or create) the
rcfile for your shell.Typingecho $SHELLin your Terminal tells youwhich shell you’re using.If you’re using Bash,edit$HOME/.bash_profileor$HOME/.bashrc.If you’re using Z shell, edit$HOME/.zshrc.If you’re using a different shell, the file pathand filename will be different on your machine. Add the following line and change
[PATH_TO_FLUTTER_GIT_DIRECTORY]to bethe path where you cloned Flutter’s git repo:- Run
source $HOME/.<rc file>to refresh the current window,or open a new terminal window toautomatically source the file. Verify that the
flutter/bindirectoryis now in your PATH by running:Verify that the
fluttercommand is available by running:
Note: As of Flutter’s 1.19.0 dev release, the Flutter SDK contains the dart command alongside the flutter command so that you can more easily run Dart command-line programs. Downloading the Flutter SDK also downloads the compatible version of Dart, but if you’ve downloaded the Dart SDK separately, make sure that the Flutter version of dart is first in your path, as the two versions might not be compatible. The following command (on macOS, linux, and chrome OS), tells you whether the flutter and dart commands originate from the same bin directory and are therefore compatible. (Some versions of Windows support a similar where command.)
As shown above, the two commands don’t come from the same bin directory. Update your path to use commands from /path-to-flutter-sdk/bin before commands from /usr/local/bin (in this case). After updating your shell for the change to take effect, running the which or where command again should show that the flutter and dart commands now come from the same directory.
To learn more about the dart command, run dart -h from the command line, or see the dart tool page.
Platform setup
macOS supports developing Flutter apps in iOS, Android,and the web (technical preview release).Complete at least one of the platform setup steps now,to be able to build and run your first Flutter app.
iOS setup
Install Xcode
To develop Flutter apps for iOS, you need a Mac with Xcode installed.
- Install the latest stable version of Xcode(using web download or the Mac App Store).
Configure the Xcode command-line tools to use thenewly-installed version of Xcode byrunning the following from the command line:
This is the correct path for most cases,when you want to use the latest version of Xcode.If you need to use a different version,specify that path instead.
- Make sure the Xcode license agreement is signed byeither opening Xcode once and confirming or running
sudo xcodebuild -licensefrom the command line.
Versions older than the latest stable version may still work,but are not recommended for Flutter development.Using old versions of Xcode to target bitcode is notsupported, and is likely not to work.
With Xcode, you’ll be able to run Flutter apps onan iOS device or on the simulator.
Set up the iOS simulator
To prepare to run and test your Flutter app on the iOS simulator,follow these steps:
On your Mac, find the Simulator via Spotlight orby using the following command:
- Make sure your simulator is using a 64-bit device(iPhone 5s or later) by checking the settings inthe simulator’s Hardware > Device menu.
- Depending on your development machine’s screen size,simulated high-screen-density iOS devicesmight overflow your screen. Grab the corner of thesimulator and drag it to change the scale. You can alsouse the Window > Physical Size or Window > Pixel Accurateoptions if your computer’s resolution is high enough.
- If you are using a version of Xcode olderthan 9.1, you should instead set the device scalein the Window > Scale menu.
Create and run a simple Flutter app
To create your first Flutter app and test your setup,follow these steps:
Create a new Flutter app by running the following from thecommand line:
A
my_appdirectory is created, containing Flutter’s starter app.Enter this directory:To launch the app in the Simulator,ensure that the Simulator is running and enter:
Deploy to iOS devices
To deploy your Flutter app to a physical iOS deviceyou’ll need to set up physical device deployment in Xcodeand an Apple Developer account. If your app is using Flutter plugins,you will also need the third-party CocoaPods dependency manager.
Install Android Studio For Mac
You can skip this step if your apps do not depend onFlutter plugins with native iOS code.Install and set up CocoaPods by running the following commands:
Note: The default version of Ruby requires
sudoto install the CocoaPods gem. If you are using a Ruby Version manager, you may need to run withoutsudo.Follow the Xcode signing flow to provision your project:
- Open the default Xcode workspace in your project byrunning
open ios/Runner.xcworkspacein a terminalwindow from your Flutter project directory. - Select the device you intend to deploy to in the devicedrop-down menu next to the run button.
- Select the
Runnerproject in the left navigation panel. - In the
Runnertarget settings page,make sure your Development Team is selected.The UI varies depending on your version of Xcode.- For Xcode 10, look under General > Signing > Team.
- For Xcode 11 and newer, look underSigning & Capabilities > Team.
When you select a team,Xcode creates and downloads a Development Certificate,registers your device with your account,and creates and downloads a provisioning profile (if needed).
- To start your first iOS development project,you might need to sign intoXcode with your Apple ID. Development and testing is supported for any Apple ID.Enrolling in the Apple Developer Program is required todistribute your app to the App Store.For details about membership types,see Choosing a Membership.
The first time you use an attached physical device for iOSdevelopment, you need to trust both your Mac and theDevelopment Certificate on that device.Select
Trustin the dialog prompt whenfirst connecting the iOS device to your Mac.Then, go to the Settings app on the iOS device,select General > Device Managementand trust your Certificate.For first time users, you may need to selectGeneral > Profiles > Device Management instead.
If automatic signing fails in Xcode, verify that the project’sGeneral > Identity > Bundle Identifier value is unique.
- Open the default Xcode workspace in your project byrunning
Start your app by running
flutter runor clicking the Run button in Xcode.
Android setup
Note: Flutter relies on a full installation of Android Studio to supply its Android platform dependencies. However, you can write your Flutter apps in a number of editors; a later step discusses that.
Install Android Studio
- Download and install Android Studio.
- Start Android Studio, and go through the ‘Android Studio Setup Wizard’.This installs the latest Android SDK, Android SDK Command-line Tools,and Android SDK Build-Tools, which are required by Flutterwhen developing for Android.
Set up your Android device
To prepare to run and test your Flutter app on an Android device,you need an Android device running Android 4.1 (API level 16) or higher.
- Enable Developer options and USB debugging on your device.Detailed instructions are available in theAndroid documentation.
- Windows-only: Install the Google USBDriver.
- Using a USB cable, plug your phone into your computer. If prompted on yourdevice, authorize your computer to access your device.
- In the terminal, run the
flutter devicescommand to verify thatFlutter recognizes your connected Android device. By default,Flutter uses the version of the Android SDK where youradbtool is based. If you want Flutter to use a different installationof the Android SDK, you must set theANDROID_SDK_ROOTenvironmentvariable to that installation directory.
Set up the Android emulator
To prepare to run and test your Flutter app on the Android emulator,follow these steps:
- EnableVM accelerationon your machine.
- Launch Android Studio, click the AVD Managericon, and select Create Virtual Device…
- In older versions of Android Studio, you should insteadlaunch Android Studio > Tools > Android > AVD Manager and selectCreate Virtual Device…. (The Android submenu is only presentwhen inside an Android project.)
- If you do not have a project open, you can choose Configure > AVD Manager and select Create Virtual Device…
- Choose a device definition and select Next.
- Select one or more system images for the Android versions you wantto emulate, and select Next.An x86 or x86_64 image is recommended.
- Under Emulated Performance, select Hardware - GLES 2.0 to enablehardwareacceleration.
Verify the AVD configuration is correct, and select Finish.
For details on the above steps, see ManagingAVDs.
- In Android Virtual Device Manager, click Run in the toolbar.The emulator starts up and displays the default canvas for yourselected OS version and device.
Web setup
Install Android Emulator For Mac
Flutter has early support for building web applications using thebeta channel of Flutter. To add support for web development, followthese instructions when you’ve completed the setup above.
Install Android For Pc
Next step
Install Mac Os On Android
Set up your preferred editor.
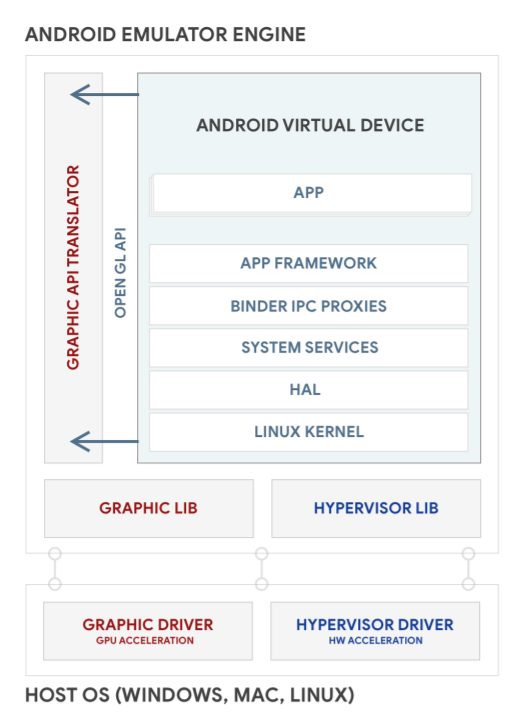
-->This article explains how to use the Android Device Manager to createand configure Android Virtual Devices (AVDs) that emulate physical Androiddevices. You can use these virtual devices to run and test your appwithout having to rely on a physical device.
After you have verified that hardware acceleration is enabled (asdescribed inHardware Acceleration for Emulator Performance),the next step is to use the Android Device Manager (also referred toas the Xamarin Android Device Manager) to create virtual devices thatyou can use to test and debug your app.
Android Device Manager on Windows
This article explains how to use the Android Device Manager to create,duplicate, customize, and launch Android virtual devices.
You use the Android Device Manager to create and configure AndroidVirtual Devices (AVDs) that run in theAndroid Emulator.Each AVD is an emulator configuration that simulates a physical Androiddevice. This makes it possible to run and test your app in a variety ofconfigurations that simulate different physical Android devices.
Requirements
To use the Android Device Manager, you will need the following items:
Visual Studio 2019 Community, Professional, or Enterprise.
OR Visual Studio 2017 version 15.8 or later is required. Visual StudioCommunity, Professional, and Enterprise editions are supported.
Visual Studio Tools for Xamarin version 4.9 or later.
The Android SDK must be installed (seeSetting up the Android SDK for Xamarin.Android).Be sure to install the Android SDK at its default location if itis not already installed: C:Program Files (x86)Androidandroid-sdk.
The following packages must be installed (via theAndroid SDK Manager):
- Android SDK Tools version 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 27.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 27.0.3 or later
- Android Emulator 27.2.7 or later.
These packages should be displayed with Installed status as seen inthe following screenshot:
Launching the Device Manager
Launch the Android Device Manager from the Tools menu byclicking Tools > Android > Android Device Manager:
If the following error dialog is presented on launch, see theTroubleshooting section for workaroundinstructions:
Main Screen
When you first launch the Android Device Manager, it presents a screenthat displays all currently-configured virtual devices. For eachvirtual device, the Name, OS (Android Version), Processor,Memory size, and screen Resolution are displayed:
When you select a device in the list, the Start button appears onthe right. You can click the Start button to launch the emulatorwith this virtual device:
After the emulator starts with the selected virtual device, theStart button changes to a Stop button that you can use to haltthe emulator:
New Device
To create a new device, click the New button (located in the upperright-hand area of the screen):
Clicking New launches the New Device screen:
To configure a new device in the New Device screen, use thefollowing steps:
Give the device a new name. In the following example, the new deviceis named Pixel_API_27:
Select a physical device to emulate by clicking the Base Devicepull-down menu:
Select a processor type for this virtual device by clicking theProcessor pull-down menu. Selecting x86 will provide thebest performance because it enables the emulator to take advantageof hardware acceleration.The x86_64 option will also make use of hardware acceleration,but it runs slightly slower than x86 (x86_64 is normallyused for testing 64-bit apps):
Select the Android version (API level) by clicking the OSpull-down menu. For example, select Oreo 8.1 - API 27 to createa virtual device for API level 27:
If you select an Android API level that has not yet been installed, theDevice Manager will display A new device will be downloadedmessage at the bottom of the screen – it will download andinstall the necessary files as it creates the new virtual device:
If you want to include Google Play Services APIs in your virtualdevice, enable the Google APIs option. To include the GooglePlay Store app, enable the Google Play Store option:
Note that Google Play Store images are available only for some basedevice types such as Pixel, Pixel 2, Nexus 5, and Nexus 5X.
Edit any properties that you need to modify. To make changes toproperties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Add any additional properties that you need to explicitly set. TheNew Device screen lists only the most commonly-modifiedproperties, but you can click the Add Property pull-down menu(at the bottom) to add additional properties:
You can also define a custom property by selecting Custom... atthe top of the property list.
Click the Create button (lower right-hand corner) to create thenew device:
You might get a License Acceptance screen. Click Accept ifyou agree to the license terms:
The Android Device Manager adds the new device to the list ofinstalled virtual devices while displaying a Creating progressindicator during device creation:
When the creation process is complete, the new device is shown inthe list of installed virtual devices with a Start button,ready to launch:
Edit Device
To edit an existing virtual device, select the device and click theEdit button (located in the upper right-hand corner of the screen):
Clicking Edit launches the Device Editor for the selected virtual device:
The Device Editor screen lists the properties of the virtual deviceunder the Property column, with the corresponding values of each property inthe Value column. When you select a property, a detailed descriptionof that property is displayed on the right.
To change a property, edit its value in the Value column.For example, in the following screenshot the hw.lcd.density propertyis being changed from 480 to 240:
After you have made the necessary configuration changes, click the Save button.For more information about changing virtual device properties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Additional Options
Additional options for working with devices are available from theAdditional Options (…) pull-down menu in the upperright-hand corner:
The additional options menu contains the following items:
Duplicate and Edit – Duplicates the currently-selecteddevice and opens it in the New Device screen with a differentunique name. For example, selecting Pixel_API_27 and clickingDuplicate and Edit appends a counter to the name:
Reveal in Explorer – Opens a Windows Explorer window in thefolder that holds the files for the virtual device. For example,selecting Pixel_API_27 and clicking Reveal in Explorer opensa window like the following example:
Factory Reset – Resets the selected device to its defaultsettings, erasing any user changes made to the internal state of thedevice while it was running (this also erases the currentQuick Bootsnapshot, if any). This change does not alter modifications that youmake to the virtual device during creation and editing. A dialog boxwill appear with the reminder that this reset cannot be undone. ClickFactory Reset to confirm the reset:
Delete – Permanently deletes the selected virtual device. Adialog box will appear with the reminder that deleting a devicecannot be undone. Click Delete if you are certain that you wantto delete the device.
Note
If you are using a Mac with an Apple chip, such as the M1, you will need to install the Android Emulator for M1 preview from GitHub.
Android Device Manager on macOS
This article explains how to use the Android Device Manager to create,duplicate, customize, and launch Android virtual devices.
You use the Android Device Manager to create and configure AndroidVirtual Devices (AVDs) that run in theAndroid Emulator.Each AVD is an emulator configuration that simulates a physical Androiddevice. This makes it possible to run and test your app in a variety ofconfigurations that simulate different physical Android devices.
Requirements
To use the Android Device Manager, you will need the following items:

Visual Studio for Mac 7.6 or later.
The Android SDK must be installed (seeSetting up the Android SDK for Xamarin.Android).
The following packages must be installed (via theAndroid SDK Manager):
- SDK tools version 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 28.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 26.0.3 or later
These packages should be displayed with Installed status as seen inthe following screenshot:
Launching the Device Manager
Launch the Android Device Manager by clicking Tools > Device Manager:
If the following error dialog is presented on launch, see theTroubleshooting section for workaroundinstructions:
Main Screen
When you first launch the Android Device Manager, it presents a screenthat displays all currently-configured virtual devices. For eachvirtual device, the Name, OS (Android Version), Processor,Memory size, and screen Resolution are displayed:
When you select a device in the list, the Play button appears onthe right. You can click the Play button to launch the emulatorwith this virtual device:
After the emulator starts with the selected virtual device, thePlay button changes to a Stop button that you can use to haltthe emulator:
When you stop the emulator, you may get a prompt asking if you want to savethe current state for the next quick boot:
Saving the current state will make the emulator boot faster when this virtualdevice is launched again. For more information about Quick Boot, seeQuick Boot.
New Device
To create a new device, click the New Device button (located in the upperleft-hand area of the screen):
Clicking New Device launches the New Device screen:
Use the following steps to configure a new device in the New Devicescreen:
Install Android On Mac
Give the device a new name. In the following example, the new deviceis named Pixel_API_27:
Select a physical device to emulate by clicking the Base Devicepull-down menu:
Select a processor type for this virtual device by clicking theProcessor pull-down menu. Selecting x86 will provide thebest performance because it enables the emulator to take advantageof hardware acceleration.The x86_64 option will also make use of hardware acceleration,but it runs slightly slower than x86 (x86_64 is normallyused for testing 64-bit apps):
Select the Android version (API level) by clicking the OSpull-down menu. For example, select Oreo 8.1 - API 27 to createa virtual device for API level 27:
If you select an Android API level that has not yet been installed,the Device Manager will display A new device will be downloadedmessage at the bottom of the screen – it will download andinstall the necessary files as it creates the new virtual device:
If you want to include Google Play Services APIs in your virtualdevice, enable the Google APIs option. To include the GooglePlay Store app, enable the Google Play Store option:
Note that Google Play Store images are available only for some basedevice types such as Pixel, Pixel 2, Nexus 5, and Nexus 5X.
Edit any properties that you need to modify. To make changes toproperties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Add any additional properties that you need to explicitly set. TheNew Device screen lists only the most commonly-modifiedproperties, but you can click the Add Property pull-down menu(at the bottom) to add additional properties:
You can also define a custom property by clicking Custom...at the top of this property list.
Click the Create button (lower right-hand corner) to create thenew device:
The Android Device Manager adds the new device to the list ofinstalled virtual devices while displaying a Creating progressindicator during device creation:
When the creation process is complete, the new device is shown inthe list of installed virtual devices with a Start button,ready to launch:
Edit Device
To edit an existing virtual device, select the Additional Optionspull-down menu (gear icon) and select Edit:
Clicking Edit launches the Device Editor for the selected virtual device:
The Device Editor screen lists the properties of the virtual deviceunder the Property column, with the corresponding values of each property inthe Value column. When you select a property, a detailed descriptionof that property is displayed on the right.
To change a property, edit its value in the Value column.For example, in the following screenshot the hw.lcd.density propertyis being changed from 480 to 240:
After you have made the necessary configuration changes, click the Save button.For more information about changing virtual device properties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Additional Options
Additional options for working with a device are available from thepull-down menu located to the left of the Play button:
The additional options menu contains the following items:
Edit – Opens the currently-selected device in the deviceeditor as described earlier.
Duplicate and Edit – Duplicates the currently-selecteddevice and opens it in the New Device screen with a differentunique name. For example, selecting Pixel 2 API 28 and clickingDuplicate and Edit appends a counter to the name:
Reveal in Finder – Opens a macOS Finder window in thefolder that holds the files for the virtual device. For example,selecting Pixel 2 API 28 and clicking Reveal in Finder opensa window like the following example:
Factory Reset – Resets the selected device to its defaultsettings, erasing any user changes made to the internal state of thedevice while it was running (this also erases the currentQuick Bootsnapshot, if any). This change does not alter modifications that youmake to the virtual device during creation and editing. A dialog boxwill appear with the reminder that this reset cannot be undone. ClickFactory Reset to confirm the reset.
Delete – Permanently deletes the selected virtual device. Adialog box will appear with the reminder that deleting a devicecannot be undone. Click Delete if you are certain that you wantto delete the device.
Troubleshooting
The following sections explain how to diagnose and work around problemsthat may occur when using the Android Device Manager to configurevirtual devices.
Android SDK in Non-Standard Location
Typically, the Android SDK is installed at the following location:
C:Program Files (x86)Androidandroid-sdk
If the SDK is not installed at this location, you may get this error when you launchthe Android Device Manager:
To work around this problem, use the following steps:
From the Windows desktop, navigate toC:UsersusernameAppDataRoamingXamarinDeviceManager:
Double-click to open one of the log files and locate the Configfile path. For example:
Navigate to this location and double-click user.config to open it.
In user.config, locate the
<UserSettings>element and add anAndroidSdkPath attribute to it. Set this attribute to the pathwhere the Android SDK is installed on your computer and save thefile. For example,<UserSettings>would look like the following ifthe Android SDK was installed at C:ProgramsAndroidSDK:
After making this change to user.config, you should be able tolaunch the Android Device Manager.
Wrong Version of Android SDK Tools
If Android SDK tools 26.1.1 or later is not installed, you may see thiserror dialog on launch:
If you see this error dialog, click Open SDK Manager to open theAndroid SDK Manager. In the Android SDK Manager, click the Toolstab and install the following packages:

- Android SDK Tools 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 27.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 27.0.3 or later
Snapshot disables WiFi on Android Oreo
If you have an AVD configured for Android Oreo with simulated Wi-Fi access,restarting the AVD after a snapshot may cause Wi-Fi access to become disabled.
To work around this problem,
Select the AVD in the Android Device Manager.
From the additional options menu, click Reveal in Explorer.
Navigate to snapshots > default_boot.
Delete the snapshot.pb file:
Restart the AVD.
After these changes are made, the AVD will restart in a state thatallows Wi-Fi to work again.
Wrong Version of Android SDK Tools
Virtual Android On Mac Free
If Android SDK tools 26.1.1 or later is not installed, you may see thiserror dialog on launch:
If you see this error dialog, click OK to open the Android SDKManager. In the Android SDK Manager, click the Tools tab andinstall the following packages:
- Android SDK Tools 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 28.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 26.0.3 or later
Snapshot disables WiFi on Android Oreo
If you have an AVD configured for Android Oreo with simulated Wi-Fi access,restarting the AVD after a snapshot may cause Wi-Fi access to become disabled.
To work around this problem,
Select the AVD in the Android Device Manager.
From the additional options menu, click Reveal in Finder.
Navigate to snapshots > default_boot.
Delete the snapshot.pb file:
Restart the AVD.
After these changes are made, the AVD will restart in a state thatallows Wi-Fi to work again.
Generating a Bug Report
If you find a problem with the Android Device Manager thatcannot be resolved using the above troubleshooting tips, please file abug report by right-clicking the title bar and selecting Generate BugReport:
If you find a problem with the Android Device Manager thatcannot be resolved using the above troubleshooting tips, please file abug report by clicking Help > Report a Problem:
Summary
Virtual Android On Android
This guide introduced the Android Device Manager available in VisualStudio Tools for Xamarin and Visual Studio for Mac. It explainedessential features such as starting and stopping the Android emulator,selecting an Android virtual device (AVD) to run, creating new virtualdevices, and how to edit a virtual device. It explained how toedit profile hardware properties for further customization, and itprovided troubleshooting tips for common problems.
Related Links
Related Video
Virtual Android On Mac Desktop
Find more Xamarin videos on Channel 9 and YouTube.